Microbiology Test 5
Quiz Summary
0 of 20 Questions completed
Questions:
Information
You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
Quiz is loading…
You must sign in or sign up to start the quiz.
You must first complete the following:
Results
Results
0 of 20 Questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You have reached 0 of 0 point(s), (0)
Earned Point(s): 0 of 0, (0)
0 Essay(s) Pending (Possible Point(s): 0)
Categories
- Not categorized 0%
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- Current
- Review
- Answered
- Correct
- Incorrect
-
Question 1 of 20
1. Question
Which 2 diseases are usually preceded by infection with the organism seen in the image below?
 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 2 of 20
2. Question
A common cause of acute exudative pharyngitis is:
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 3 of 20
3. Question
A 15-year-old is admitted to the ER with severe sinusitis. Aspiration specimens from the nasal passage reveal a pure culture of alpha-hemolytic, depressed center colonies with a distinctive mucoid appearance on a blood agar plate. Gram stains of the colonies are shown below:
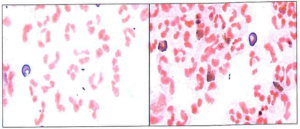
Which of the following could aid in the identification of the organism recovered?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 4 of 20
4. Question
A 6-year-old male presents to his pediatrician with a severe case of tonsillitis. The physician collects a throat swab specimen and orders a GAS (group A Streptococcus) probe test. The following day, the probe comes back negative. A culture is requested. The laboratory results are shown in this table:
test
result
catalase
negative
bacitracin disk
sensitive
hippurate hydrolysis
negative
CAMP test
negative
PYR
negative
Gram stain
gram-positive cocci in chains
Which of the following organisms is most likely causing the tonsillitis?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 5 of 20
5. Question
Small, pleomorphic gram-negative bacilli are isolated from an eye culture. They grow only on chocolate agar and are oxidase-variable. The most likely organism is:
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 6 of 20
6. Question
An isolate on chocolate agar from a patient with epiglottitis is suggestive of Haemophilus species. Additional testing shows that the isolate required NAD for growth and is nonhemolytic. The organism is most likely Haemophilus:
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 7 of 20
7. Question
A 3-year-old unimmunized female presents to the ER with a severe cough, fever, and flu-like symptoms. The parents report that the child had vomited a few times due to the severe coughing. A nasopharyngeal swab is used to collect the specimen and planted on a chocolate, Bordet-Gengou, and Regan Lowe media. After 5 days of incubation, colonies grow on all of the media, with the growth on Bordet-Gengou described as “drops of mercury. “The Gram stain shows minute coccobacilli that are catalase-positive and oxidase-positive. The most likely identification of this isolate is:
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 8 of 20
8. Question
A Gram stain performed on a sinus aspirate reveals gram-negative diplococci and PMNs. Oxidase testing is positive and carbohydrate degradation tests are inert. The organism most likely is:
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 9 of 20
9. Question
Establishing the pathogenicity of a microorganism isolated from a child’s throat and identified as Corynebacterium diphtheriae would depend upon:
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 10 of 20
10. Question
Chlamydia trachomatis infections have been implicated in:
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 11 of 20
11. Question
A liquid fecal specimen from a 3-month-old infant is submitted for culture. The stool culture should detect Salmonella, Shigella and:
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 12 of 20
12. Question
When performing a stool culture, a colony type typical of an enteric pathogen is subcultured on a blood agar plate. The resulting pure culture is screened with several tests to obtain the results shown in this table:
test
result
TSI
acid butt, alkaline slant, no gas, no H2S
phenylalanine deaminase
negative
motility
nonmotile
serological typing
Shigella flexneri(Shigella subgroup B)
The serological typing is verified with new kit and controls. The best course of action would be to:
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 13 of 20
13. Question
MacConkey media for screening suspected cases of hemorrhagic E. coli O157:H7must contain:
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 14 of 20
14. Question
An isolate from a stool culture gives the growth characteristics and biochemical reactions shown in this table:
test
result
MacConkey agar
colorless colonies
Hektoen agar
yellow-orange colonies
TSI
acid slant/acid butt, no gas, no H2S
urea
positive
These screening reactions are consistent with which of these enteric pathogens?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 15 of 20
15. Question
Which of the following organisms can grow in the small bowel and cause diarrhea in children, traveler’s diarrhea, or a severe cholera-like syndrome through the production of enterotoxins?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 16 of 20
16. Question
Shigella species characteristically are:
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 17 of 20
17. Question
Gram-negative bacilli have been isolated from feces, and the confirmed biochemical reactions fit those of Shigella. The organism does not agglutinate in Shigella antisera. What should be done next?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 18 of 20
18. Question
Biochemical reactions of an organism are consistent with Shigella. A suspension is tested in antiserum without resulting agglutination. However, after 15 minutes of boiling, agglutination occurs in group-D antisera. The Shigella species is:
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 19 of 20
19. Question
An 8-year-old girl is admitted to the hospital with a 3-day history of fever, abdominal pain, diarrhea, and vomiting. A stool culture grows many lactose-negative colonies that yielded the laboratory results shown in this table:
test
result
oxidase
negative
TSI
acid slant/acid butt
indole
negative
urease
positive
ornithine decarboxylase
positive
sucrose
positive
H2S
negative
motility at 25℃
positive
The most probable identification of this organism is:
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 20 of 20
20. Question
A fecal specimen, inoculated to xylose lysine deoxycholate (XLD) and Hektoen enteric (HE) produced colonies with black centers. Additional testing results are shown in this table:
biochemical screen
result
serological test
result
Glucose fermentation
positive
polyvalent
no agglutination
H2S
positive
group A
no agglutination
lysine decarboxylase
positive
group B1
no agglutination
urea
negative
group C
no agglutination
ONPG
negative
group D
no agglutination
indole
positive
group Vi
no agglutination
The most probable identification is:
CorrectIncorrect